Generate Gpg Key For Github
Yubikey, Smart Cards, OpenSC and GnuPG are pain in the ass to get working. Those snippets here sould help alleviate pain.
To reset and disable not used modes on Yubikey you need the ykman program
Jan 24, 2018 A shell script that automates the process of signing Git sources via GPG - NicoHood/gpgit. Upload to Github; 1. Generate a new GPG key 1.1 Strong, unique, secret passphrase. Make sure that your new passphrase for the GPG key meets high security standards. If the passphrase/key is compromised all of your signatures are compromised too. Many Git servers authenticate using SSH public keys. In order to provide a public key, each user in your system must generate one if they don’t already have one. This process is similar across all operating systems. First, you should check to make sure you don’t already have a key.
You can install it using those commands
GnuPG usage only needs CCID mode to be enabled. FIDO mode can also be enabled for WebAuthn
- Jul 04, 2019 The commands will work for both GPG and GPG2. I use Julian's key for the examples. His key id is 2AD3FAE3. You should substitute with the appropriate key id when running the commands. Signing the key. List the keys currently in your keyring: gpg -list-keys. I want to sign Julian's key, so I pull it into my keyring: gpg -recv-keys 2AD3FAE3.
- If you don't already have an SSH key, you must generate a new SSH key.If you're unsure whether you already have an SSH key, check for existing keys. If you don't want to reenter your passphrase every time you use your SSH key, you can add your key to the SSH agent, which manages your SSH keys and remembers your passphrase.
- I want to sign my GitHub commits with GnuPG. So I'm trying to generate a GPG key as instructed in this article. But the problem is when I run this command on the terminal: gpg -full-generate-ke.
- In order to use GPG keys with Bitbucket Server, you'll need generate a GPG key locally, add it to your Bitbucket Server account, and also set it up for use with Git. If you already have a GPG key ready to go, you can jump straight to the Add a GPG key to Bitbucket Server section.
- Jun 30, 2017 Keeping a project build in a manageable time range is an important prerequisite for an efficient software development workflow. The more complex projects are the more time, automation effort and tools required to develop and maintain an efficient build pipeline. Regardless of a scale and type of a project the core principle of avoiding unnecessary work is worth applying. This tutorial.
Yubikey OpenPGP applet that is used by GnuPG can be configured with
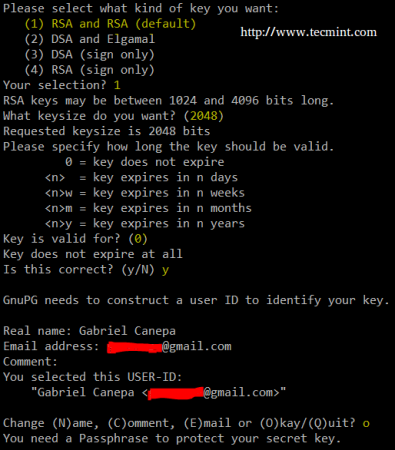
Make sure that gnupg, pcscd and scdaemon are installed
GnuPG Smart Card stack looks something like this
Now we have to tell scdaemon to use pcsc interface instead of the default direct connect mode.
Under Ubuntu libpcsclite.so is in package called libpcsclite1.dpkg -L libpcsclite1 command can show the location of the lib.
GnuPG Trust Model
Turn on ssh like trust on first use (tofu)
After changing gpg configuration files, it's a good idea to restart gpg-agent.
If everything went well then running following command should show something like this
Debuging
Test if Yubikey is detected
pcsc-tools package contains pcsc_scan program that can be used to check that Yubikey is detected.
and then run
Now you should see Card inserted and removed events on your terminal when connectingand removing Yubikey.
Restart everything
Smart Card middleware
gpg-agent
Check the logs
Run journalctl in another terminal window and look for scdaemon log lines
If you see sharing violation messages then something else is probably trying to use the yubikey via opensc.Check getting-estonian-id-card-and-gnupg-scdaemon-yubikey-work-together
Switch from OpenSSH ssh-agent to GnuPG as ssh-agent
Temporarily
First get you need to get GnuPG agent-ssh-socket path
That should return something like this
And then you can set that path as SSH_AUTH_SOCK environment variable
After that ssh-add -l shoud show your Yubikey.
Permanent
Getting Estonian ID card and GnuPG scdaemon Yubikey work together.
Estonian ID card uses opensc project to access private keys on the smart card.Opensc also supports Yubikey and that will create conflicts with GnuPG scdaemon.
To fix it you can just disable Yubikey in opensc.
To make coperation between opensc and scdaemon even better then you have to patch scdaemon touse shared access mode, Arch Linux wiki has a short paragraph about that here https://wiki.archlinux.org/index.php/GnuPG#Shared_access_with_pcscd.
gpg -k or gpg --list-keys - List stored public keys
gpg -K or gpg --list-private-keys - List all stored private keys, # means private key is unavailable, > means private key is on a smartcard
- Generate 2048bit RSA master key with Certify(Master) and Sign permissions, expire key after 2 years
- Add a 2048bit RSA encryption subkey that expires after 2 years
where master_key_fingerprint is a 40 char hex string shown when running gpg -K
man page says that you can use -e option to convert private and public keys to other formats, that seems to be wrong. Insteadyou can use -p option to request changing the password but not actually setting the password.
Monkeysphere project includes a pem2openpgp command that can be used to import ssh private keys to gnupg keyring.
The imported key is stored without encryption, add it with those commands:
If you are running Windows and PuTTYTray for SSH, you can use the built-in key generator from PuTTY to create a new key pair. Click the Keygen button at the bottom of the PuTTY Configuration window to get started. Then in the Key Generator window, check that the Type of key to generate at the bottom is set to SSH-2 RSA. The older SSH-1 was the first version on. How to generate an SSH key and add your public key to the server for authentication Step 1: Check for SSH Keys. First, check for existing SSH keys on your computer. Step 2: Generate a new SSH key. With your command line tool still open, enter the text shown below. Step 3: Add your key. Apr 02, 2019 Home Linux Basics: How To Create and Install SSH Keys on the Shell. Generating a key pair offers users two lengthy strings of characters corresponding to a public as well as a private key. Users can, thus, place the public key on any server, and subsequently, unlock the same by connecting to it with a client that already possesses the. Generate ssh keys for a user. Remember that the.ssh directory cannot be readable or writeable by anyone but the user, and the user's home directory cannot be writeable by anyone but the user. Likewise, permissions must be tight on the private key, as well: Read/write for only the user, and the.ssh directory and private keyfile must be owned by the user. You should check for existing SSH keys on your local computer. You can use an existing SSH key with Bitbucket Server if you want, in which case you can go straight to either SSH user keys for personal use or SSH access keys for system use. Open a command prompt, and run.
and then use passwd command and type the same password as your master key
After importing you can use normal gpg --edit-key command to change parameters on this key. GnuPG 2.1 also allows you to move the imported key to be one of your subkeys for authentication. https://security.stackexchange.com/a/160847
Move the key
- Get the imported key keygrip value
gpg --with-keygrip -k gpg --expert --edit-key <master_key_id>wheremaster_key_idis a 40 char hex string shown when runninggpg -K- type
addkey - select
(13) Existing key - Copy and Paste imported ssh key keygrip
- Toggle off all capabilities and enable authenticate capability and finish
- Set key valid time to 2 years with
2y - Confirm key creation and type your master key password
- Type
saveto save and exit from edit menu
Delete old public ssh key
This key is no longer needed
where ssh_key_id is a 40 char hex string shown when running gpg -K
Before moving private keys to yubikey you must make a backup of private keys so that when you lose or break your yubikeyyou could move the same keys to a new yubikey.
Exported keys are encrypted with your master password.
Its also a good idea to print your private keys on a paper because files can bitrot and become unusable after some time.
and then use keytocard command to move the primary key to card.Then select first sub key with key 1 and then move that to card with keytocard.Then unselect first key with command key and then select second subkey with key 2 and then do keytocard. After that save and you are done.
scdaemon with shared access for ubuntu 18.04https://d.arti.ee/scdaemon_2.2.4-1ubuntu1.2_amd64.deb
What do ssb and other mean in gpg --list-keys output
# after sec/ssb means that secret key is unavailable, maybe it was exported and then deleted
> after sec/ssb means that secret key is on a smartcard/yubikey
A readme and a script to generate PGP keys using GnuPG, using the current best practices.
Its goal is to provide a concise and up-to-date description of best practices regarding the usage of GnuPG. A basic understanding of public key cryptography, and GnuPG in particular is assumed.
If something is not clear or you're new to PGP, then make sure to start with the Glossary below.
Some quick insights
- Public key cryptography happens between two encryption keys, which is not necessarily only two humans, unless enough care has been taken when exchanging public keys and to keep the secret keys indeed secret.
- In a digital networked world it's not possible to delete any published information, it must be assumed to be just there forever. This also applies to PGP keys.
- Properly authenticated revocation requests can be published, though. If such requests are digitally signed (authenticated), then they will be honored by programs handling e.g. PGP keys (key servers, client programs), and the revoked data will be ignored/hidden from the user accordingly.
- Having a separately stored revocation certificate in your backup comes very handy if your key gets compromised or lost. By publishing it you can tell your peers that your key should not be used anymore.
- The most precious part of a PGP key block is its master signing key.
- The master signing key of a PGP key block is rarely needed (mostly when editing/extending the PGP key block itself and when signing other people's keys).
- You can only trust you generated PGP key to the extent you trust the software environment and/or the computer generating it. Opensource is a minimum in security, so use a Linux live cd or something similar from a trusted source to generate and/or use your master signing key, preferably while being offline (see live CD's in the Glossary)!
- Specialized hardware solutions offer much better protection for secret keys. See below.
- If you forget the passphrase for your already published key, and you don't have a revocation certificate either, then your key will be lingering on the keyservers confusing your peers, who will annoy you by sending you messages you cannot read.
- Passphrases: three to five word long sentences that you make up yourself (based on a non-trivial vocabulary, personal experiences, dreams, preferably with s0me typ0s) are easier to remember than a bunch of random characters, and are better passphrases. You can even build a little story around them to have separate but semantically interconnected passphrases (for the keys, for the revocation certificate, etc.). A vivid dream or delightful fantasies can be a good basis for something you won't forget.. :)
- ..but at the end of the day it'll always be a tradeoff between security and convenience. Assess your risks and act accordingly.
The PGP algorithm needs an extra parameter, a key, to sign or encrypt data. That parameter is a cryptographic keypair, usually one of the subkeys from a PGP key block. New subkeys can be freely generated and published, so forward secrecy can be achieved by publishing new subkeys, as long as the secret part of the master signing keypair has not been compromised. Therefore the most precious part of a PGP key block is its master signing key, because whenever new information is attached to the key block (e.g. a new subkey is generated), this new data must be signed by the secret part of the master signing keypair, otherwise conforming programs will reject the new unsigned or improperly signed part of the PGP key block. In this scheme publishing valid additions to the key block is only possible by people who know the secret part of the master signing key. This is ideally you, and you only.
So, to conclude: keep the secret part of your master signing key safe!
Github Generate Gpg Key
Generating a key
The aim is to generate a digital identity that can serve to identify you and to facilitate secret communication with you in the future.
Things to consider:
- If a valid signing subkey exists, then the master signing key is rarely used (only to sign internal parts of the key block itself, when explicitly selected, or when signing other people's keys), so the size of the signatures it generates is not a major concern.
- Having a strong master signing key (and taking good care of it) can provide a long time span for your digital identity (possibly 10+ years) and for forward secrecy.
- The security of RSA keys does not scale well beyond 2048 bits, use ECC (Elliptic curve cryptography) instead as recommended. Unfortunately it requires GnuPG 2.1+ (2014 Nov).
- Longer signing keys generate longer signatures.
- Signature length: RSA > DSA = ECDSA (Elliptic Curve DSA) (but there's more to this story).
- Some GnuPG configuration parameters affect newly generated keys (although not in a permanent way); e.g. see setpref to set the preferred hash algorithms for identities here.
Even more thoughts here.
Using GnuPG
GnuPG properly operates with a PGP key block that is missing the secret part of its master signing key, as long as it's not needed for an operation. Therefore it's a good idea not to store the secret part of the master signing key in the regularly used gpg home directory, but rather generate and handle it in a safer environment; e.g. generate and handle it using a live CD without Internet connection, and store it on a pendrive dedicated to this purpose. Then only attach it when needed (e.g. when signing other people's keys or when your own keyblock needs to be modified).
This script generates (with defaults in parens):
- a master signing key (RSA 4096 bit, no expiration date marked)
- a subkey for signing (RSA 4096 bit, 3 years)
- a subkey for encryption (RSA 2048 bit, 3 years)
- export the secret part of the master signing key into the file
secret-master-key.gpg - export the secret parts of the two generated subkeys into the file
secret-subkeys.gpg - export the public parts of all the three generated keys into the file
public-keys.gpg - generate and symmetrically encrypt a revocation certificate into the file
revocation-certificate-for-[keyid]-passphrase-protected.gpg - (planned: support for
ssss-splitto generate secret sharing to backup the master key and the revocation certificate in a distributed manner)
Once the exported files have been generated, you can import them into the gpg homedir's on your devices (by default ~/.gnupg). Where you should import and what depends on the level of security you want to achieve, but keeping the master key offline is advised as described above.
When writing a keygen, the author will identify the algorithm used in creating a valid cd key. Once the algorithm is identified they can then incorporate this into the keygen. If you search a warez download site for 'metro 2033 cd key generator keygen', this often means your download includes a keygen. Metro 2033 cd key generator free download. Aug 29, 2017 Thanks to this fantastic Metro 2033 Generator you can generate different Keys for you and your friends!The only Metro 2033 code generator that works.No download required.We just released a new leaked Metro 2033 Serial Key Generator that can generate keys for Windows PC, Xbox One and Playstation 4.Metro 2033 Keygen is a simple-to-use program. Metro 2033 License Activation Key generator! Metro 2033 Keygen is here and it is FREE and 100% working and legit. Before our system send cd key, you will need to pass this human verification step. When writing a keygen, the author will identify the algorithm used in creating a valid cd key. Once the algorithm is identified they can then incorporate this into the keygen. If you search a warez download site for 'metro 2033 cd key keygen', this often means your download includes a keygen. May 19, 2017 Metro 2033 Crack Patch And CD Key Generator for free here! Links always updated and working! Right here in few clicks! Download Now. Metro 2033 Serial Key Download Code Crack key generator Full Game Torrent skidrow Origin Key and Steam Online Code Avaiable. Metro 2033 Serial Key Cd Key Free Download Crack Full Game Metro 2033 Serial Cd Key.
(the '#' character in the output shows that the secret part of the master signing key is missing)
SmartCards and other hardware keys
SmartCards and USB cryptographic tokens are specialized simple computers that perform cryptographic operations. They are designed to keep the secret keys secret even against physical attacks. They are much more secure than storing a key on a personal computer, but they are not flawless ⁽¹⁾⁽²⁾. Usually they can store three separate keys for signing, encryption, and authentication. The secret keys can be either uploaded or generated on the cards themselves, so that they never get exposed to less secure environments.
- The OpenPGP Card version 2.0 - a SmartCard with extensive documentation and thus stable Linux support. You can also get one by joining the FSFE Fellowship. Supports three 4096 bit keys and on-card key generation⁽¹⁾.
- Crypto Stick - a tiny OpenSource USB computer and firmware with an integrated proprietary smart card chip. Supports OATH TOTP as described here.
- gnuk - a portable OpenSource implementation of the OpenPGP Card specification that can run on e.g. this tiny ARM based OpenSource USB computer.
Some laptops have internal smart card readers, and higher security external readers have their own PIN entry keyboard.
Further information on using smart cards on Linux: Debian wiki, Using an OpenPGP SmartCard, OpenSC – tools and libraries for smart cards, GnuPG wiki.
Glossary
Generate Gpg Key For Github Download
- PGP key - It's usually a shorthand for PGP key block, which will be the case in this document, too. Not to be confused with asymmetric cryptographic keypairs, which are merely parts of PGP key blocks.
- PGP key block - a complex structure of information (normally stored in ~/.gnupg/). Examples of the information it can contain: multiple cryptographic (sub)keys; multiple identities (email addresses, photgraphs, etc); digital signatures on various parts of the key block (potentially made by other people's keys, e.g. to communicate the belief to the rest of the world that the same real world person owns the listed digital identities, and also the secret part of the key).
- subkey - PGP key blocks can have, among other things, multiple asymmetric cryptographic keypairs. One such asymmetric cryptographic keypair is mandatory for normal operation. It's called the master signing key, and it's used to sign various information inside the key block, e.g. identities and/or other cryptographic keys, which are called subkeys.
- asymmetric cryptographic keypair - they are basically pairs of very big interconnected random numbers, one of them should be made public, while the other one should be kept secret. Asymmetric encryption algorithms use the public part to encrypt data and to verify signature blocks, while use the secret part to decrypt data and to generate signature blocks.
- OATH is short for Initiative for Open Authentication. Among other things it defines a Time-based One-time Password (TOTP) authentication standard, supported by more and more websites.
- Live CD is a bootable read-only operating system, like these security focused Linux Live CDs (bootable from USB pendrives also):
- Liberté Linux.
Alternatives and/or further reading
Credits
Written by Attila Lendvai attila.lendvai@gmail.com (Key fingerprint: 2FA1 A9DC 9C1E BA25 A59C 963F 5D5F 45C7 DFCD 0A39).

If you've found this useful, then tips are welcome:
What Is A Gpg Key
- Bitcoin (BTC):
1Ej8SeMNTkwjSwhKLu7H1XLVRPZ3HUjM4J(0 BTC as of 2014-01-18) - Ripple (XRP):
r33NEgyd7HqvrUeB98rQ4VoBxP438gC74Q(0 XRP as of 2014-01-18) - Paypal: (0 USD as of 2015-11-10)