Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Key
- Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Key Mean
- Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Key Software
- Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Key Generator
- Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Keys
- Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Key Password
ESXi and vCenter Server support standard X.509 version 3 (X.509v3) certificates to encrypt session information sent over Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol connections between components. If SSL is enabled, data is private, protected, and cannot be modified in transit without detection.
- Apr 03, 2012 Do not create the Symmetric or Asymmetric keys in system databases such as Master, Model, MSDB and Tempdb as it is not a good practice to create any user-defined objects in system databases. For symmetric key encryption, use AES128 bits and above. For asymmetric key encryption, use 2048 bits and above.
- The two main types of keys in cryptographic systems are symmetric-key and public-key (also known as asymmetric-key). Types Symmetric key. In symmetric-key schemes, the encryption and decryption keys are the same. Communicating parties must have the same key.
The following options are available when you generate new encryption keys for your Virtual SAN cluster. If you generate a new KEK, all hosts in the Virtual SAN cluster receive the new KEK from the KMS. Each host's DEK is re-encrypted with the new KEK. If you choose to re-encrypt all data using new keys, a new KEK and new DEKs are generated. This symmetric key is encrypted by using an asymmetric public key that corresponds to the computer and the user account that is used to run the Report Server service. When you change the user account that is used to run the Report Server service, the report server cannot use the asymmetric public key to decrypt the symmetric key.
Open PuttyGen. Move the mouse over the progress bar. Check the Type of key and number of bytes to use. Here's how to create an ssh key with Putty:. Install. 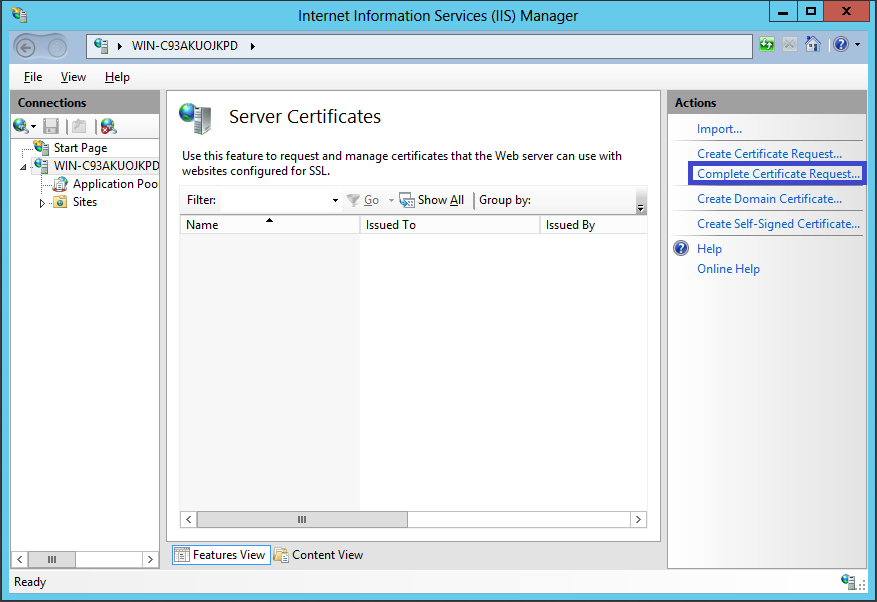
All network traffic is encrypted as long as the following conditions are true:
Jul 22, 2019 Failed to generate VirtualCenter symmetric encryption key. Installing vCenter Server 6.5 U2 or 6.7 fails during firstboot with this message in the UI similar to: Failed to generate VirtualCenter symmetric encryption key. Apr 03, 2012 The following best practices can be followed when using Symmetric and Asymmetric keys. Asymmetric encryption and decryption are relatively resource-intensive, but they provide a higher level of security than symmetric encryption. An asymmetric key can be used to encrypt a symmetric key for storage in a database. For symmetric encryption I need a key, which I need to store somewhere. From a similar questions I have a few options, but none is applicable in my case: Tie the encryption key to your admin login. I don't trust the currently logged user. In fact, I want to hide this from anyone, but App1. Tie the encryption key.
You did not change the Web proxy service to allow unencrypted traffic for the port.
■ | Your firewall is configured for medium or high security. |
Certificate checking is enabled by default and SSL certificates are used to encrypt network traffic. However, ESXi and vCenter Server use automatically generated certificates that are created as part of the installation process and stored on the server system. These certificates are unique and make it possible to begin using the server, but they are not verifiable and are not signed by a trusted-well-known certificate authority (CA). These default certificates are vulnerable to possible man-in-the-middle attacks.
To receive the full benefit of certificate checking, particularly if you intend to use encrypted remote connections externally, install new certificates that are signed by a valid internal certificate authority or purchase a certificate from a trusted security authority. Replacing vCenter Server certificates is described in the vSphere Examples and Scenarios documentation.
Generate private key using keytool key. If the self-signed certificate is used, clients receive a warning about the certificate. To address this issue, install a certificate that is signed by a recognized certificate authority. If CA-signed certificates are not installed, all communication between vCenter Server and vSphere Clients is encrypted using a self-signed certificate. These certificates do not provide the authentication security you might need in a production environment.
The certificate consists of two files: the certificate itself (rui.crt) and the private-key file (rui.key).
Location | |
|---|---|
ESXi 5.0 | /etc/vmware/ssl/ |
vCenter Server (Windows 2008) | C:Program DataVMwareVMware VirtualCenterSSL |
vCenter Server (Windows 2003) | C:Documents and SettingsAll UsersApplication DataVMwareVMware VirtualCenterSSL |
Symmetric-key algorithms[a] are algorithms for cryptography that use the same cryptographic keys for both encryption of plaintext and decryption of ciphertext. The keys may be identical or there may be a simple transformation to go between the two keys.[1] The keys, in practice, represent a shared secret between two or more parties that can be used to maintain a private information link.[2] This requirement that both parties have access to the secret key is one of the main drawbacks of symmetric key encryption, in comparison to public-key encryption (also known as asymmetric key encryption).[3][4]
Types[edit]
Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Key Mean
Symmetric-key encryption can use either stream ciphers or block ciphers.[5]
- Stream ciphers encrypt the digits (typically bytes), or letters (in substitution ciphers) of a message one at a time. An example is the Vigenère Cipher.
- Block ciphers take a number of bits and encrypt them as a single unit, padding the plaintext so that it is a multiple of the block size. Blocks of 64 bits were commonly used. The Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) algorithm approved by NIST in December 2001, and the GCM block cipher mode of operation use 128-bit blocks.
Implementations[edit]
Examples of popular symmetric-key algorithms include Twofish, Serpent, AES (Rijndael), Blowfish, CAST5, Kuznyechik, RC4, DES, 3DES, Skipjack, Safer+/++ (Bluetooth), and IDEA.[6]
Cryptographic primitives based on symmetric ciphers[edit]
Symmetric ciphers are commonly used to achieve other cryptographic primitives than just encryption.[citation needed]
Encrypting a message does not guarantee that this message is not changed while encrypted. Hence often a message authentication code is added to a ciphertext to ensure that changes to the ciphertext will be noted by the receiver. Message authentication codes can be constructed from symmetric ciphers (e.g. CBC-MAC).[citation needed]
However, symmetric ciphers cannot be used for non-repudiation purposes except by involving additional parties.[7] See the ISO/IEC 13888-2 standard.
Another application is to build hash functions from block ciphers. See one-way compression function for descriptions of several such methods.
Construction of symmetric ciphers[edit]
Many modern block ciphers are based on a construction proposed by Horst Feistel. Feistel's construction makes it possible to build invertible functions from other functions that are themselves not invertible.[citation needed]
Security of symmetric ciphers[edit]
Symmetric ciphers have historically been susceptible to known-plaintext attacks, chosen-plaintext attacks, differential cryptanalysis and linear cryptanalysis. Careful construction of the functions for each round can greatly reduce the chances of a successful attack.[citation needed]
Key management[edit]
Key establishment[edit]
Symmetric-key algorithms require both the sender and the recipient of a message to have the same secret key.All early cryptographic systems required one of those people to somehow receive a copy of that secret key over a physically secure channel.
Nearly all modern cryptographic systems still use symmetric-key algorithms internally to encrypt the bulk of the messages, but they eliminate the need for a physically secure channel by using Diffie–Hellman key exchange or some other public-key protocol to securely come to agreement on a fresh new secret key for each message (forward secrecy).
Key generation[edit]
When used with asymmetric ciphers for key transfer, pseudorandom key generators are nearly always used to generate the symmetric cipher session keys. However, lack of randomness in those generators or in their initialization vectors is disastrous and has led to cryptanalytic breaks in the past. Therefore, it is essential that an implementation use a source of high entropy for its initialization.[8][9][10]
Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Key Software
Reciprocal cipher[edit]
Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Key Generator
A reciprocal cipher is a cipher where, just as one enters the plaintext into the cryptography system to get the ciphertext, one could enter the ciphertext into the same place in the system to get the plaintext. A reciprocal cipher is also sometimes referred as self-reciprocal cipher.
Practically all mechanical cipher machines implement a reciprocal cipher, a mathematical involution on each typed-in letter.Instead of designing two kinds of machines, one for encrypting and one for decrypting, all the machines can be identical and can be set up (keyed) the same way.[11]
Examples of reciprocal ciphers include:
- Beaufort cipher[12]
- Enigma machine[13]
- Marie Antoinette and Axel von Fersen communicated with a self-reciprocal cipher.[14]
- the Porta polyalphabetic cipher is self-reciprocal.[15]
- Purple cipher[16]
Practically all modern ciphers can be classified as either a stream cipher, most of which use a reciprocol XOR cipher combiner, or a block cipher, most of which use use Feistel cipher or Lai–Massey scheme with a reciprocal transformation in each round.
Notes[edit]
- ^Other terms for symmetric-key encryption are secret-key, single-key, shared-key, one-key, and private-key encryption. Use of the last and first terms can create ambiguity with similar terminology used in public-key cryptography. Symmetric-key cryptography is to be contrasted with asymmetric-key cryptography.
References[edit]
Failed To Generate Virtualcenter Symmetric Encryption Keys
- ^Kartit, Zaid (February 2016). 'Applying Encryption Algorithms for Data Security in Cloud Storage, Kartit, et al'. Advances in ubiquitous networking: proceedings of UNet15: 147.
- ^Delfs, Hans & Knebl, Helmut (2007). 'Symmetric-key encryption'. Introduction to cryptography: principles and applications. Springer. ISBN9783540492436.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^Mullen, Gary & Mummert, Carl (2007). Finite fields and applications. American Mathematical Society. p. 112. ISBN9780821844182.CS1 maint: uses authors parameter (link)
- ^'Demystifying symmetric and asymmetric methods of encryption'. Cheap SSL Shop. 2017-09-28.
- ^Pelzl & Paar (2010). Understanding Cryptography. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. p. 30.
- ^Roeder, Tom. 'Symmetric-Key Cryptography'. www.cs.cornell.edu. Retrieved 2017-02-05.
- ^14:00-17:00. 'ISO/IEC 13888-2:2010'. ISO. Retrieved 2020-02-04.
- ^Ian Goldberg and David Wagner.'Randomness and the Netscape Browser'.January 1996 Dr. Dobb's Journal.quote:'it is vital that the secret keys be generated from an unpredictable random-number source.'
- ^Thomas Ristenpart , Scott Yilek.'When Good Randomness Goes Bad: Virtual Machine Reset Vulnerabilities and Hedging Deployed Cryptography (2010)'CiteSeerx: 10.1.1.183.3583quote from abstract:'Random number generators (RNGs) are consistently a weak link in the secure use of cryptography.'
- ^'Symmetric Cryptography'. James. 2006-03-11.
- ^Greg Goebel.'The Mechanization of Ciphers'.2018.
- ^'.. the true Beaufort cipher. Notice that we have reciprocal encipherment; encipherment and decipherment are identically the same thing.'--Helen F. Gaines.'Cryptanalysis: A Study of Ciphers and Their Solution'.2014.p. 121.
- ^Greg Goebel.'The Mechanization of Ciphers'.2018.
- ^Friedrich L. Bauer.'Decrypted Secrets: Methods and Maxims of Cryptology'.2006.p. 144
- ^David Salomon.'Coding for Data and Computer Communications'.2006.p. 245
- ^Greg Goebel.'US Codebreakers In The Shadow Of War'.2018.